Trading credit
It doesn't matter if the market is trading up, down or sideways. There is an options trading strategy to make money.
My list of forex bonuses
Hence the popularity of options. Again, if trading credit spreads for a living is your income, the limited risk is ideal. In fact, you're able to discuss this in our trading room.
Trading credit spreads for a living and how to get started
Here are some important things to know if you're looking to trade credit spreads for a living. 1. You need a large trading account with at least $10,000, but ideally more than $25,000. 2. Several trades need to be active. 3. Look to take profits around 50%. 4. Keep losses small and cut them quickly. 5. Rolling a credit spread is great way to limit losses and even turn losing trades into winners.
Trading credit spreads for a living & how to get started
Did you know that trading credit spreads for a living is a way to generate income while minimizing risk? Options trading allows you to make money in any market.
It doesn't matter if the market is trading up, down or sideways. There is an options trading strategy to make money. Hence the popularity of options.
Options give you the right but not the obligation to buy (call) or sell (put) a stock at a specified price. Read our post on put and call options explained.
One options contract controls 100 shares of a stock. As a result, trading options is cheaper. However, options have more moving parts than a stock. These moving parts affect the price of a stock much more than trading shares.
This can be both good and bad. You can have a bigger return on your investment but also lose a lot more. So if you're trading options, trading credit spreads for a living allows you to do trade a strategy that minimizes your risk.
1. Credit: trading credit spreads for a living
You can't buy one option for one stock and sell an option for another stock. That just becomes buying and selling naked calls and/or puts.
With a credit spread, the money in credited to your account at the start of the trade. This strategy was designed to make a profit when the spreads between the two options narrows. Credit spreads can be bullish or bearish. As a result, you need to make sure you choose the correct direction when you're trading credit spreads for a living.
2. The pros and cons
Trading credit spreads for a living may limit risk. Although, the trade off is the limiting or profit potential. However, if this is how you generate income, the limited risk is better for you.
Sure a naked call or put has the possibility for unlimited profit. However, the risk of a bad loss is real. As a result of having many moving parts to options, things like time decay, intrinsic value and implied volatility can impact how much you make or lose. Read our post on the implied volatility formula and its meaning.
Spreads cap loss if the stock moves dramatically in the opposite direction. We all know the stock market moves off of emotions. Any news, whether good or bad, will move the market or a stock.
There's never going to be perfect market conditions for trading. In fact, the ability to minimize risk is more important than trying to hit a home run on every trade.
If you've looked at the charts and see a clear chance to make a large profit by placing a naked options trade, then take that risk. If you're relying on your trading profits to make a living, then take the safer way.
Sure your profit potential is limited but you can still make a few hundred dollars a trade without putting up a lot of money.
Again, if trading credit spreads for a living is your income, the limited risk is ideal. In fact, you're able to discuss this in our trading room.
3. The types of credit spreads
There are different types of credit spreads. The credit spread also known as a vertical spread. A credit put spread also known as a bull put spread. The credit call spread is also known as a bear call spread.
A credit spread or vertical spread is simultaneously buying and selling calls or puts with different strike prices. A bull put spread is a bullish position where you make more money on the short put.
A bull put spread is best used when the market consolidates or the stock you want to trade is rising. In essence, you can use this strategy for two different occasions
A bear call spread is a bearish position where the money comes from the short call. You use this position when you believe the market or stock is hitting its peak.
Make sure you practice trading these spreads before using real money. You want to see how they work and if you're using them correctly with the way the markets and stocks are moving.
Our service is a great place to come in order to learn more about trading credit spreads for a living.
4. The goal of trading credit spreads for a living
Trading credit spreads for a living means your goal is to get a net credit. This is your income and you can't make any more money than that. The way you get a credit is by the premium you pay for when you purchase the option is lower than the premium you pay for the option you sell.
To keep your entire credit you want the spread you're selling to expire worthless. However nothing is ever perfect. If you have a good profit then it might be a good thing to go ahead and take it. You never go broke taking profit.
Credit trading
For financing needs that conventional products cannot satisfy
Cash and working capital are key to the success of any company. The financing of trade in your company’s lifecycle, whether you’re buying or selling goods, services or commodities, enables you to offer more competitive terms to win business and mitigate payment risk. There are a number of instruments you can use to finance trade flows.
Some of the benefits
Trade finance credit
Extensive african presence
Credit-linked notes
Credit risk analysis
Do you need to enhance your working capital?
Liquidity is an important factor in any business, giving you the ability to quickly convert assets such as investments, accounts receivable, and inventory into cash.
As africa’s dominant provider of credit-based liquidity, our innovative structured credit products are delivered through innovative credit combinations that provide you with access to both african and global asset pools that you could not access independently.
As a leading trader and market-maker in both developed and emerging market cash and derivative products we specialise in enhancing credit yield in customised structures that match your risk-return profiles.
- Trade finance credit: one of the biggest challenges faced by companies trading in africa is the gap in trade finance, especially in relation to credit availability.
- Managing credit risk: you need to stay on top of business credit risk management by having access to the information you need on market changes.
- Credit-linked notes: as with many other credit derivatives, these are used to help manage both your exposure to credit risk and your balance sheet.
- Trusted expertise: we understand that you need a banking partner that you can trust. Our expertise in africa and globally, provides you with trusted insights and skills to navigate credit opportunities.
International trade involves buying and selling across countries that have very different financial and legal systems, environments and cultures.
Our unique and extensive presence across the african continent, combined with our proven capabilities and expertise in developed capital markets, provide the insight and skills you need to successfully link emerging and frontier credit opportunities with developed market credit, through transactions that are globally compliant.
- African economies are impacted differently by global macroeconomic factors, which necessitates a case-by-case approach when analysing credit risk.
- Our in-depth knowledge of discrete african credit markets allows us to access credit on-the-ground.
- We have pioneered the structuring of multiple credit linked note programmes, in both ZAR and non-ZAR listed notes, that leverage african and global credit, and we are currently among the top 15 global issuers of credit notes.
Do you need to enhance your working capital?
Liquidity is an important factor in any business, giving you the ability to quickly convert assets such as investments, accounts receivable, and inventory into cash.
As africa’s dominant provider of credit-based liquidity, our innovative structured credit products are delivered through innovative credit combinations that provide you with access to both african and global asset pools that you could not access independently.
As a leading trader and market-maker in both developed and emerging market cash and derivative products we specialise in enhancing credit yield in customised structures that match your risk-return profiles.
- Trade finance credit: one of the biggest challenges faced by companies trading in africa is the gap in trade finance, especially in relation to credit availability.
- Managing credit risk: you need to stay on top of business credit risk management by having access to the information you need on market changes.
- Credit-linked notes: as with many other credit derivatives, these are used to help manage both your exposure to credit risk and your balance sheet.
- Trusted expertise: we understand that you need a banking partner that you can trust. Our expertise in africa and globally, provides you with trusted insights and skills to navigate credit opportunities.
International trade involves buying and selling across countries that have very different financial and legal systems, environments and cultures.
Our unique and extensive presence across the african continent, combined with our proven capabilities and expertise in developed capital markets, provide the insight and skills you need to successfully link emerging and frontier credit opportunities with developed market credit, through transactions that are globally compliant.
- African economies are impacted differently by global macroeconomic factors, which necessitates a case-by-case approach when analysing credit risk.
- Our in-depth knowledge of discrete african credit markets allows us to access credit on-the-ground.
- We have pioneered the structuring of multiple credit linked note programmes, in both ZAR and non-ZAR listed notes, that leverage african and global credit, and we are currently among the top 15 global issuers of credit notes.
Trade credit
What is a trade credit?
A trade credit is a business-to-business (B2B) agreement in which a customer can purchase goods on account without paying cash up front, paying the supplier at a later scheduled date. Usually businesses that operate with trade credits will give buyers 30, 60, or 90 days to pay, with the transaction recorded through an invoice. Trade credit can be thought of as a type of 0% financing, increasing a company’s assets while deferring payment for a specified value of goods or services to some time in the future and requiring no interest to be paid in relation to the repayment period.
Trade credit
Understanding trade credit
A trade credit is an advantage for a buyer. In some cases, certain buyers may be able to negotiate longer trade credit repayment terms which provides an even greater advantage. Often, sellers will have specific criteria for qualifying for trade credit.
A B2B trade credit can help a business to obtain, manufacture, and sell goods before ever having to pay for them. This allows businesses to receive a revenue stream that can retroactively cover costs of goods sold. Walmart is one of the biggest utilizers of trade credit, seeking to pay retroactively for inventory sold in their stores. International business deals also involve trade credit terms. In general, if trade credit is offered to a buyer it typically always provides an advantage for a company’s cash flow.
The number of days for which a credit is given is determined by the company allowing the credit and is agreed upon by both the company allowing the credit and the company receiving it. Trade credit can also be an essential way for businesses to finance short-term growth. Because trade credit is a form of credit with no interest, it can often be used to encourage sales.
Since trade credit puts suppliers at somewhat of a disadvantage, many suppliers use discounts when trade credits are involved to encourage early payments. A supplier may give a discount if a customer pays within a certain number of days before the due date. For example, a 2% discount if payment is received within 10 days of issuing a 30-day credit. This discount would be referred to as 2%/10 net 30 or simply just 2/10 net 30.
Key takeaways
- Trade credit is a type of commercial financing in which a customer is allowed to purchase goods or services and pay the supplier at a later scheduled date.
- Trade credit can be a good way for businesses to free up cash flow and finance short-term growth.
- Trade credit can create complexity for financial accounting.
- Trade credit financing is usually encouraged globally by regulators and can create opportunities for new financial technology solutions.
Trade credit accounting
Trade credits are accounted for by both sellers and buyers. Accounting with trade credits can differ based on whether a company uses cash accounting or accrual accounting. Accrual accounting is required for all public companies. With accrual accounting a company must recognize revenues and expenses at the time they are transacted.
Trade credit invoicing can make accrual accounting more complex. If a public company offers trade credits it must book the revenue and expenses associated with the sale at the time of the transaction. When trade credit invoicing is involved, companies do not immediately receive cash assets to cover expenses. Therefore, companies must account for the assets as accounts receivable on their balance sheet.
With trade credit there is the possibility of default. Companies offering trade credits also usually offer discounts which means they can receive less than the accounts receivable balance. Both defaults and discounts can require the need for accounts receivable write-offs from defaults or write-downs from discounts. These are considered liabilities a company must expense.
Alternatively, trade credit is a useful option for businesses on the buying side. A company can obtain assets but would not need to credit cash or recognize any expenses immediately. In this way a trade credit can act like a 0% loan on the balance sheet. The company’s assets increase but cash does not need to be paid until some time in the future and no interest is charged during the repayment period. A company only needs to recognize the expense when cash is paid using the cash method or when revenue is received using the accrual method. Overall, these activities greatly free up cash flow for the buyer.
Trade credit trends
Trade credit is most rewarding for businesses that do not have a lot of financing options. In financial technology, new types of point of sale financing options are being provided for businesses to utilize in place of trade credits. Many of these fintech firms partner with sellers at the point of sale to provide 0% or low interest financing on purchases. These partnerships help to alleviate trade credit risks for sellers while also supporting growth for buyers.
Trade credit has also brought about new financing solutions for sellers in the form of accounts receivable financing. Accounts receivable financing, also known as invoice financing or factoring, is a type of financing that provides businesses with capital in relation to their trade credit, accounts receivable balances.
From an international standpoint, trade credit is encouraged. The world trade organization reports that 80% to 90% of world trade is in some way reliant on trade finance. Trade finance insurance is also a part of many trade finance discussions globally with many new innovations. Liquidx for example now offers an electronic marketplace focused on trade credit insurance for global participants.
Research conducted by the U.S. Federal reserve bank of new york also highlights some important insights. The 2019 small business credit survey finds that trade credit finance is the third most popular financing tool used by small businesses with 13% of businesses reporting that they utilize it.
Related concepts and other considerations
Trade credit has a significant impact on the financing of businesses and is therefore linked to other financing terms and concepts. Other important terms that affect business financing are credit rating, trade line, and buyer’s credit.
A credit rating is an overall assessment of the creditworthiness of a borrower, whether a business or individual, based on financial history that includes debt repayment timeliness and other factors. Without a good credit rating, trade credit may not be offered to a business. If businesses do not pay trade credit balances according to agreed terms, penalties in the form of fees and interest are usually incurred. Sellers can also report delinquencies on trade credit which may affect a buyer’s credit rating. Delinquencies affecting a buyer’s credit rating can also affect their ability to obtain other types of financing as well.
A trade line, or tradeline, is a business credit account record provided to a business credit reporting agency. For large businesses and public companies, trade lines can be followed by rating agencies such as standard & poor’s, moody’s, or fitch.
Buyer’s credit is related to international trade and is essentially a loan given to specifically finance the purchase of capital goods and services. Buyer’s credit involves different agencies across borders and typically has a minimum loan amount of several million dollars.
Crédit agricole trading
Il trading online è uno degli strumenti finanziari più diffusi e ricercati del momento per iniziare ad investire in autonomia. Per questo, molte banche come crédit agricole, hanno affiancato ai tradizionali servizi di internet banking anche le funzionalità delle piattaforme d’investimento virtuale.
Crédit agricole è una di queste. Grazie all’offerta di cariparma nowbanking i correntisti dell’istituto possono dedicarsi anche al trading, investendo su numerosi mercati nazionali ed esteri.

Trading con crédit agricole: conviene davvero?
Nel 2007 crédit agricole assume il controllo di cariparma, divenendo il primo gruppo europeo nel retail banking. Per stare al passo con i tempi, la banca ha studiato anche una piattaforma per i clienti che vogliono operare finanziariamente.
Con il sito e l’app sempre aggiornati, le news, l’interazione con gli indici di mercato e la gestione sicura del portafoglio virtuale sono a portata di mano.
Ma iniziare a fare trading vuol dire, prima di tutto, studiare tutte le opportunità del settore e scegliere quella più coerente con le proprie possibilità d’investimento.
È necessario dare uno sguardo più approfondito all’offerta di trading di crédit agricole, e confrontarla con le prestazioni e le opportunità previste da tre broker leader nel mondo del trading online: ci riferiamo a etoro, capital.Com e IQ option.
Nota bene: tutte queste piattaforme sono regolamentate da licenza CYSEC e CONSOB per operare in italia e negli altri paesi dell’unione europea.
Ognuna mette a disposizione degli utenti conti demo gratuiti per fare pratica nei mercati finanziari, comprendere le regole del trading online e iniziare ad investire in totale sicurezza.
I metodi alternativi al trading offerto da crédit agricole: i CFD
Uno degli strumenti finanziari più ricercati dagli utenti che desiderano fare trading online è quello dei CFD (contratti per differenza).
Il motivo è semplice: si tratta di una strategia di investimento molto più accessibile e veloce di quelle tradizionali, con vantaggi rilevanti anche dal punto di vista del profitto.
Non è necessario possedere ingenti capitali o immobilizzarli per lunghi periodi, né acquistare fisicamente azioni come richiesto dal mercato reale.
I CFD, infatti, consentono al trader di scegliere su quale operazione desidera investire tenendo sempre sotto controllo la propria disponibilità economica e le prospettive di profitto.
Una volta individuata l’attività finanziaria desiderata l’utente negozia con il broker la propria posizione, aprendola per un dato intervallo di tempo prestabilito, operando su di essa sia al rialzo che al ribasso.
In questo modo, si genera profitto non soltanto quando il prezzo dell’asset cresce, ma anche quando esso cala.
Inoltre, grazie al sistema della “leva finanziaria” utilizzato da tutti i principali broker, tutti possono avvicinarsi al trading con risorse decisamente ridotte rispetto al più rigido mercato finanziario tradizionale e in tempi molto più brevi.
I costi delle singole operazioni vengono determinati di volta in volta dai broker di trading online, pur restando sempre entro alcuni parametri generali.
Le possibili variazioni dei costi, dettate dalla mancanza di contratti standard per i CFD, impongono agli utenti la necessità di individuare la piattaforma più adatta alle proprie esigenze. Esistono diversi broker, sicuri e regolamentati, fra i quali scegliere: ecco nel dettaglio quali sono.
Le alternative al trading di crédit agricole: i migliori broker online
Etoro, capital.Com e IQ option sono tre broker leader nel settore del trading online. Ognuno offre servizi ed opzioni differenziate in base agli interessi dei trader e alle opportunità del mercato, ma tutti garantiscono efficienza e sicurezza.
Tutte le piattaforme sono certificate, in base ai parametri stabiliti dall’unione europea, da cysec e CONSOB.
Il ventaglio di offerte previste da questi broker è molto ampio, e necessita di un’analisi più approfondita.
Dai conti con zero commissioni a quelli demo gratuiti ed illimitati, fino agli strumenti forex e criptovalute, ecco nel dettaglio quali sono le funzionalità messe a disposizione da ciascuna delle piattaforme citate.
Etoro: investire con zero commissioni
Etoro (visita il sito ufficiale) ha all’attivo milioni di utenti registrati da oltre 140 paesi nel mondo, e grazie anche alla solida esperienza nell’ambito del social trading è uno dei broker più affermati nel settore degli investimenti online.
La piattaforma permette di operare in azioni, CFD per coppie di valute, indici, materie prime e criptovalute: il tutto tramite i certificati di sicurezza e affidabilità sottoscritti dalle maggiori authorities del settore.
Per iniziare ad investire con etoro basta aprire un account sul sito tramite registrazione gratuita. In modo veloce ed intuitivo, saranno subito disponibili oltre 300 milioni di asset aggiornati.
Basta effettuare un primo deposito sul conto per iniziare ad aprire le proprie posizioni e operare sul mercato con un semplice click.
Come si diceva la registrazione sulla piattaforma è gratuita. Questo broker, inoltre, non prevede ulteriori costi addizionali per la gestione del profilo richiesti, invece, da qualsiasi istituto bancario.
Con etoro l’utente non dovrà prevedere nessuna commissione ticket né costi ulteriori legati alle operazioni effettuate.
Operazioni estremamente avanzate, diversificate e accessibili anche agli utenti meno esperti: questo broker prevede anche l’investimento in criptovalute.
Si tratta di uno degli strumenti più richiesti al momento dai traders. Grazie ad etoro gli utenti hanno la possibilità di creare un portafoglio personalizzato, monitorare gli scambi e interagire con altri investitori, sempre in totale sicurezza.
Un altro dei vantaggi offerti da questo broker è l’avanzato sistema di gestione degli account in ottica social.
Gli utenti iscritti possono infatti unirsi alla community di copytrader interagendo in tempo reale con i migliori traders, copiandone in maniera automatica le performance e migliorando così le proprie performances.
Capital.Com: investire con trading forex
La piattaforma di capital.Com (visita il sito ufficiale) è gestita dalla società di investimenti f1markets limited, con sede a cipro.
Gli strumenti finanziari messi a disposizione sono estremamente diversificati, fra azioni, materie prime, CFD, indici e forex. L’utente potrà monitorare in tempo reale le variazioni di prezzo degli oltre 270 asset offerti, il tutto in sicurezza e comodamente da pc, smartphone o tablet.
Uno dei punti di forza di questo broker è l’attenzione per la formazione dei propri utenti. Anche chi si affaccia da poco al mondo del trading online può investire con consapevolezza.
Nella sezione dedicata a news e approfondimenti sono disponibili decine di video ed ebook completi di analisi di mercato, glossari, lezioni di psicologia e gestione del capitale.
Un altro servizio peculiare offerto da questo broker è quello del trading con forex: investimenti e scambi in valute globali, che creano profitto dalla differenza dei prezzi di acquisto e di vendita.
Tramite le funzionalità con MT4, il broker configura le offerte in base alla variazione settimanale della valuta, ampliando e diversificando costantemente le possibilità di investimento.
IQ option: investire con le opzioni FX
IQ option (visita il sito ufficiale) opera dal 2013 nel mondo del trading online, con una media di 21 mila transazioni al giorno.
Questo broker opera, fra le altre cose, in CFD e criptovalute. Tramite la piattaforma user friendly è possibile monitorare in tempo reale l’andamento dei mercati globali.
Gli utenti ricevono notizie sui feed più seguiti del momento e sulle variazioni giornaliere degli asset, tramite un sito in italiano sempre aggiornato.
Per aprire un conto su IQ option basta un deposito di soli 10 euro. In modo sicuro, a zero commissioni, è possibile iniziare ad investire su centinaia di asset e CFD. Ma questo broker pensa anche ai meno esperti.
Con il conto demo gratuito ed illimitato, attraverso il quale imparare in sicurezza le basi del trading online prima di aprire un conto reale.
Per i più esperti, invece, oltre ad un manager attivo 24 ore su 24 per seguire le transazioni e rispondere alle domande, è prevista la funzionalità opzioni FX.
La piattaforma offre l’opportunità di chiudere la propria posizione su un dato investimento prima della scadenza temporale impostata precedentemente dal trade. In questo modo, l’utente può fare trading ad intervalli di tempo ridotti rispetto al solito.
Caratteristiche dell’offerta crédit agricole
Crédit agricole, come altri istituti di credito, va incontro alle esigenze dei clienti che desiderano iniziare ad investire online con la piattaforma cariparma nowbanking.
Iniziare a fare trading con questa banca è semplice: basta avere un conto corrente attivo e le relative credenziali di accesso all’area clienti.
Gli utenti hanno accesso agli investimenti su tutti i maggiori mercati azionari italiani ed esteri, con un canone annuo fisso e commissioni che variano in base all’operatività del profilo.
Se si desidera iniziare a fare trading con crédit agricole è necessario comparare i prezzi delle operazioni disponibili (che sono pari a zero se si sceglie un buon broker online) per valutare al meglio l’accessibilità dei servizi offerti dalla banca.
Canone annuo e commissioni crédit agricole
Il canone annuo per accedere al nowbanking di crédit agricole è di 24 euro e comprende i servizi internet e phone banking, per effettuare operazioni anche dal centralino della banca.
In questo caso, se si desidera attivare l’opzione su più numeri, è previsto un costo aggiuntivo di 5 euro. Oltre che da telefono, i clienti accedono anche alle funzionalità del sito e dell’app.
Le commissioni sulle operazioni sono fisse, e si diversificano in base al tipo di investimento:
- È previsto un costo di 10 euro per le azioni e i titoli italiani;
- Per i titoli esteri si arriva anche a 15 euro;
Inoltre, cariparma nowbanking impone un canone di abbonamento mensile aggiuntivo se si scelgono determinati asset: 4,50 euro per trading su USA NYSE, fino a 20 euro per XETRA.
Così configurata, l’offerta di crédit agricole, non risulta conveniente per gli utenti con un’operatività media di quattro o cinque operazioni giornaliere.
Considerando il canone annuo, aggiungendo le commissioni e gli ulteriori costi per accedere ad alcuni mercati, il margine di profitto si riduce troppo per chi non dispone di ingenti capitali.
Problema che invece, scegliendo altri broker certificati, viene del tutto eliminato. Clicca qui per l’offerta a zero commissioni di etoro.
Mercati su cui investire con crédit agricole
L’offerta di crédit agricole permette ai trader di operare sui principali mercati italiani ed esteri. In particolare, con costi aggiuntivi, si accede a XETRA (germania), euronext, il gran bretagna LSE, l’USA NASDAQ e l’USA NYSE.
Come per la maggior parte degli istituti bancari, però, sono assenti gli investimenti in criptovalute e le operazioni in forex.
Tutti strumenti sempre più ricercati dagli utenti, che altri broker certificati offrono a condizioni molto vantaggiose: clicca qui per accedere al sito e agli strumenti CDF di capital.Com.
Crédit agricole: piattaforme di trading
Crédit agricole ha elaborato una piattaforma studiata appositamente per i propri clienti.
Accessibile sia da smartphone che da tablet, offre news di mercato, quotazioni in tempo reale, notifiche push e alert per i titoli più importanti. Gli utenti possono inoltre gestire il portafoglio virtuale, interagire con azioni e bond e negoziare sui mercati italiano ed estero.
Tuttavia, essendo una piattaforma ad esclusivo uso dei correntisti, risulta accessibile solo da browser: strumento notoriamente più lento e meno efficiente, oltre che meno sicuro, di una piattaforma disponibile invece tramite software.
Un grande limite, da aggiungere all’assenza di materiali informativi e video, contrariamente a offerte molto meglio strutturate di ottimi broker come capital.Com.
Tutti strumenti che invece altri broker online favoriscono ed incentivano in modo sempre maggiore: clicca qui per il sito ufficiale di IQ option.
Crédit agricole: l’offerta di trading conviene?
Pur restando al passo con le crescenti richieste degli utenti interessati ad entrare nel mondo del trading online, crédit agricole perde terreno.
Questo specialmente se confrontiamo le offerte di questo istituto bancario con quelle di altri broker online certificati come etoro, capital.Com e IQ option.
Tale valutazione è riassumibile nella scarsa accessibilità agli strumenti e ai costi di gestione dei profili previsti da cariparma nowbanking.
Le alte commissioni e i canoni aggiuntivi per richiedere asset specifici rappresentano un ostacolo per chi non intende investire grandi somme di denaro, soprattutto all’inizio.
Soprattutto quando si inizia dalle basi del trading è fondamentale assicurarsi operazioni semplici e sicure. Necessità a cui altri broker vanno incontro con i conti demo gratuiti ed illimitati.
Sempre considerando le necessità degli utenti meno esperti, la piattaforma di crédit agricole non consente un’adeguata formazione prima di intraprendere il trading: elemento che invece piattaforme come etoro o capital.Com mettono al primo posto.
Come sempre nel caso del trading bancario, inoltre, l’accesso alle offerte di crédit agricole è vincolato alla fidelizzazione all’istituto bancario tramite il conto corrente.
È sicuramente più facile valutare piattaforme come IQ option, che non necessitano di ulteriori requisiti altre all’account completamente gratuito.
Crédit agricole: opinioni e considerazioni finali
In quanto piattaforma operante anche nel banking online, crédit agricole è certamente affidabile.
Tuttavia la sua offerta di trading non è accessibile per chi non dispone di ingenti capitali e non ha un’operatività estremamente alta. Gli investimenti con questo istituto, a causa dei canoni esosi, risultano poco vantaggiosi.
Trade credit
For many businesses, trade credit is an essential tool for financing growth. Trade credit is the credit extended to you by suppliers who let you buy now and pay later. Any time you take delivery of materials, equipment or other valuables without paying cash on the spot, you're using trade credit.
When you're first starting your business, however, suppliers most likely aren't going to offer you trade credit. They're going to want to make every order c.O.D. (cash or check on delivery) or paid by credit card in advance until you've established that you can pay your bills on time. While this is a fairly normal practice, you can still try and negotiate trade credit with suppliers. One of the things that will help you in these negotiations is a properly prepared financial plan.
When you visit your supplier to set up your order during your startup period, ask to speak directly to the owner of the business if it's a small company. If it's a larger business, ask to speak to the CFO or any other person who approves credit. Introduce yourself. Show the officer the financial plan you've prepared. Tell the owner or financial officer about your business, and explain that you need to get your first orders on credit in order to launch your venture.
Depending on the terms available from your suppliers, the cost of trade credit can be quite high. For example, assume you make a purchase from a supplier who decides to extend credit to you. The terms the supplier offers you are two-percent cash discount with 10 days and a net date of 30 days. Essentially, the suppliers is saying that if you pay within 10 days, the purchase price will be discounted by two percent. On the other hand, by forfeiting the two-percent discount, you're able to use your money for 20 more days. On an annualized basis, this is actually costing you 36 percent of the total cost of the items you are purchasing from this supplier! (360 ( 20 days = 18 times per year without discount; 18 ( 2 percent discount = 36 percent discount missed.)
Cash discounts aren't the only factor you have to consider in the equation. There are also late-payment or delinquency penalties should you extend payment beyond the agreed-upon terms. These can usually run between one and two percent on a monthly basis. If you miss your net payment date for an entire year, that can cost you as much as 12 to 24 percent in penalty interest.
Effective use of trade credit requires intelligent planning to avoid unnecessary costs through forfeiture of cash discounts or the incurring of delinquency penalties. But every business should take full advantage of trade that is available without additional cost in order to reduce its need for capital from other sources.
Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
Options trading 101 - the ultimate beginners guide to options
Download the 12,000 word guide
It's free
Options trading 101 - the ultimate beginners guide to options
Download the 12,000 word guide

Credit spread option strategies are hugely popular with income traders as they can generate profits in multiple conditions.
In this article I’ll briefly discuss the 3 strategies, show you how they’re set up and then I’ll show you some real examples, so you can see how each of the strategies performs relative to changes in the stock price over time.
Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit spreads
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror stories
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example
- Conclusion
Introduction
Credit spreads, or vertical spreads as they are sometimes called are high probability trades and can profit in more than one way.
They can even profit if the stock moves against you, as long as it doesn’t move too far, as you will see shortly.
Credit spreads can profit in the following ways:
- Favorable movement in the stock price
- Small, unfavourable movement in the stock price
- Time decay
- Decrease in implied volatility
The best time to enter credit spreads is when implied volatility is high. When this occurs, trades can be placed further away from the stock price giving the trade more margin for error.
What is A credit spread?
A credit spread is an option strategy that involves selling an option and then buying a further out-of-the-money option in the same expiry period.
Credit spreads are an income strategy, because premium is collected when initiating the trade. This is because the option that is being sold has a higher premium than the option that is being bought.
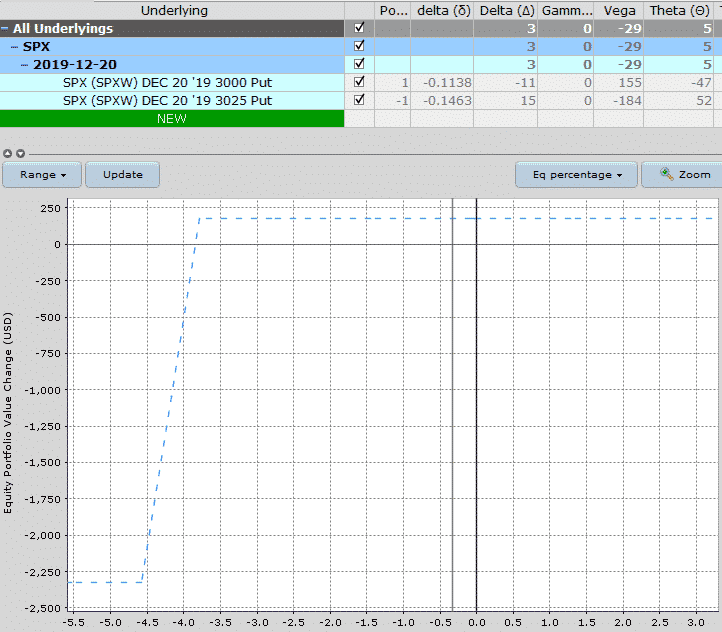
Assuming we are bullish on the S&P 500 over the next month, we could sell a put credit spread on SPX.
Typically, this would be below the market. Some people like to use the 10 delta or the 15 delta as the short strike.
Using the 15 delta, the setup would look something like this:
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $3,132
Trade set up:
Sell 1 SPX december 20th, 3025 put @ $8.30
buy 1 SPX december 20th, 3000 put @ $6.50
Premium: $180 net credit
Capital at risk: $2,320
Return potential: 7.76%
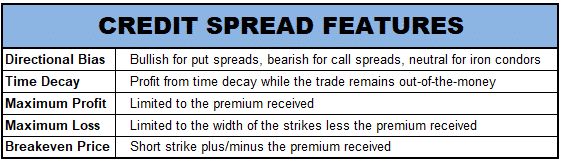
Key features of option credit spreads
Put credit spreads
Put credit spreads are a fantastic strategy because stocks tend to rise over time.
This is a strategy that you would implement if you were bullish on a stock or felt that it wouldn’t decline by too much during the trade.
A put credit spread is known as a bull put spread and is constructed by:
- Selling a put option
- Buying another put option at a lower strike price in the same expiry period
Most people trade bull put spreads as out-of-the-money spreads which gives them a good margin for error on the trade.
The further out-of-the-money the trade is placed, the less premium that is received and the higher the capital at risk in the trade.
One regular trade I like to do is a long-term bull put credit spread on dow stocks that have become oversold.
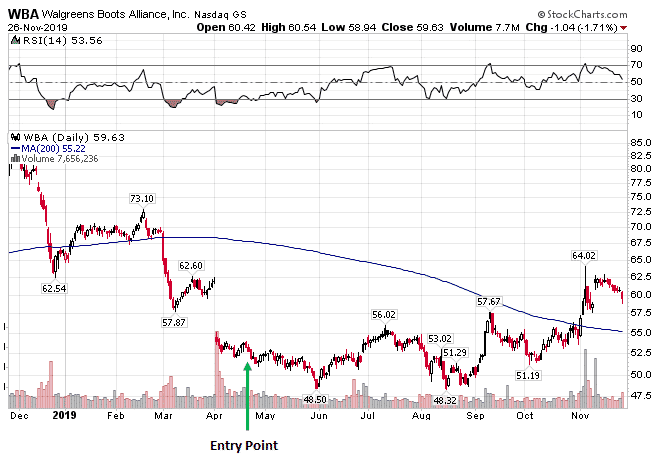
Here’s a trade from early in 2019 on WBA:
Date: april 22nd, 2019
Current price: $54.35
Trade set up:
Sell 10 WBA january 17th 2020, 40 puts @ $0.90
buy 10 WBA january 17th 2020, 35 puts @ $0.40
Premium: $500 net credit
Capital at risk: $4,500
Return potential: 11.11%
Since entering the trade WBA has reached a low of $48.32 in august and in late november was trading at $59.63 with the put credit spread currently sitting at +$440 in P&L.
I’ll look to close the trade out now as there isn’t much premium left and closing the trade can free up the capital for other trades.
Because this was such a long-term trade, it allowed me to place the spread a huge distance away from the WBA price.
At the time, the $40 strike which I sold was 25% below the stock price!
Call credit spreads
Call credit spreads are implemented by traders who think a stock will decline or not rise by much during the trade.
A call credit spread is known as a bear call spread as is constructed by:
- Selling a call option
- Buying another call option at a higher strike price in the same expiry period
The further out-of-the-money the trade is placed, the less premium is received and the higher the capital at risk in the trade.
AAPL is currently one of the most overbought stocks in the dow and looking a little toppy.
While the stock may continue to grind higher, a pullback is definitely overdue and fairly likely at some point in the in the next few weeks.
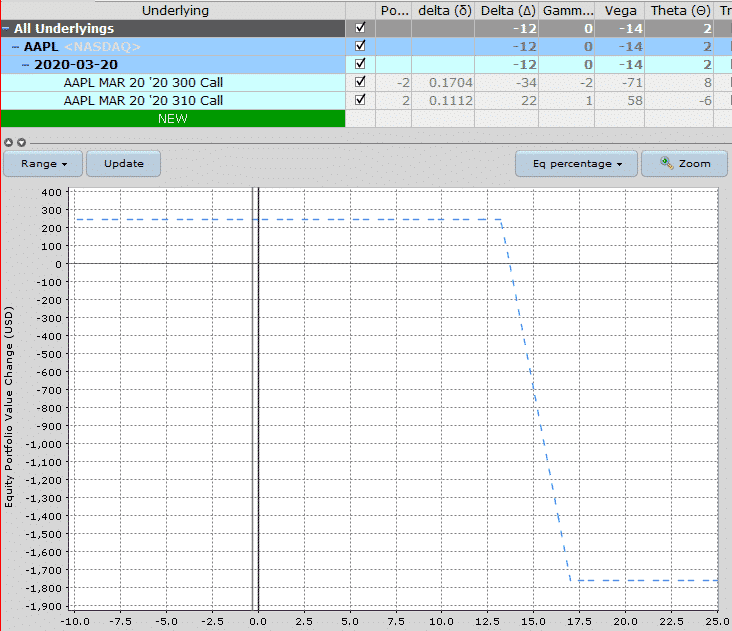
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $264
Trade set up:
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 300 calls @ $3.07
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 310 calls @ $1.85
Premium: $244 net credit
Capital at risk: $1,756
Return potential: 13.90%
The only downside with this trade is that implied volatility is currently so low in AAPL, that I can’t place the spread as far out-of-the-money as I normally could.
Still, with the short strike at $300, AAPL can rally 13.65% before the short strike is touched.
Iron condor spread
When you combine a put credit spread and a call credit spread, you get a position known as an iron condor.
This is a direction neutral trade and will profit if the stock remains between the two spreads during the course of the trade.
If you want some detailed training on iron condors, you can check out my free course here.
Let’s look at a quick example:
Using our AAPL example, we can add a put credit spread to turn it into an iron condor.
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $264
Trade set up:
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 300 calls @ $3.07
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 310 calls @ $1.85
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 230 puts @ $3.84
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 220 puts @ $2.65
Premium: $482 net credit
Capital at risk: $1,518
Return potential: 31.75%
Notice that by generating two lots of premium, we have more than doubled our return potential. You may have also noticed that the capital at risk has decreased.
This is due to the extra premium received while the spreads are the same distance apart.
As above, the only issue with this trade idea is that implied volatility is very low, so it may not be the best time for an iron condor.
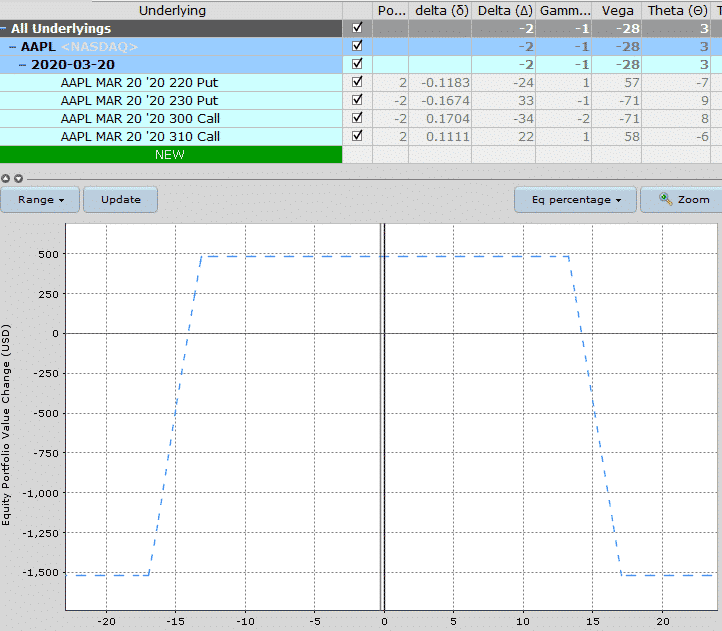
Weekly credit spreads for income
Weekly credit spreads can be excellent for generating income, but they are not without risks.
Before we look at the risks, let’s talk about the positives.
The main reason for trading weekly credit spreads is that they provide HUGE amounts of time decay, so profits can be generated very quickly.
Here’s an example of how it works.
This weekly credit spread on AAPL, selling the roughly 10 delta puts, has a theta value of 23. This means that the position will make roughly $23 per day through time decay, all else being equal.
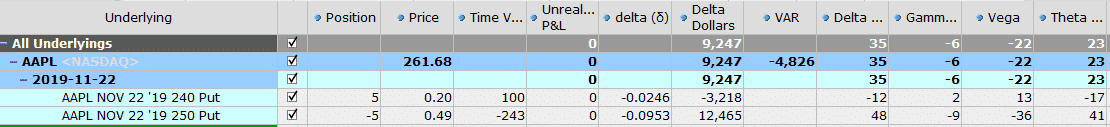
This trade is also selling the 10 delta puts but is a 65-day trade.
The time decay here is only 4$ per day.
As you can see, there is a big difference in the amount of time decay generated from weekly credit spreads compared to monthly or two-month credit spreads.
Notice the difference in gamma as well.
I won’t go into detail now, you can read more about gamma here and here . Just know that the difference between -1 gamma and -6 gamma is significant.
Beginner traders get very excited by the profit potential and fail to realize or fully understand the risk.
There are many websites and “gurus” out there claiming it’s “super easy” to make 5% per week.
Now, anyone with a basic understanding of finance understands that higher returns equal higher risk.
Therefore, if someone is claiming to make 5% per week (which equates to 260% per year), do you think there is much risk involved??
I know my readers are much too smart to fall for those sort of marketing gimmicks, but you would be surprised how many people get sucked in to this way of trading.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve spoken to traders and they all have the same story:
Weekly credit spread horror stories
The stock and timing is different, but the scenario is always the same.
“things were going great, I had 20 winning weeks in a row, and then the market made a big move and BAM, all 20 weeks’ worth of gains were gone, and then some.”
It can happen quickly as well. That gamma risk I talked about earlier, that basically means that even for a small move in the underlying stock, the P&L on the position will move wildly.
That can be great if the stock goes your way, but it can be disastrous if it moves against you.
A high gamma also means that your delta exposure will pick up steam quickly as the position moves against you.
So not only are your losses accelerating, your delta exposure is also getting bigger and bigger.
In a situation like this, there is very little you can do to adjust or save the trade. You can hope the stock reverses, but hope is not a valid strategy.
Monthly credit spreads for income
Monthly credit spreads are also a great option strategy for generating income and they move a lot slower than weekly credit spreads.
This allows you more time to adjust and can give you flexibility by allowing you to stay in the trade longer, even if the stock is moving against you.
One thing I have moved to recently is going even longer term with my credit spreads (see WBA example above).
These trades move very, very slowly, but can still generate excellent returns on an annualized basis with much less stress.
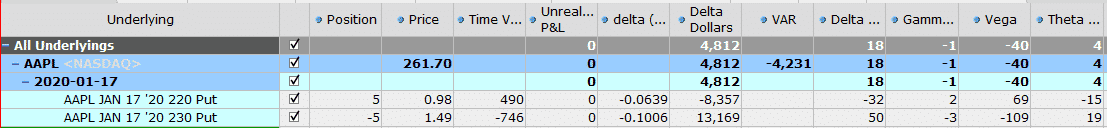
Let’s use AAPL again and compare a 1-month put credit spread and a 6-month put credit spread using the 10-delta strike as the short strike.
1-MONTH BULL PUT SPREAD
This one-month bull put spread has the potential to make $250 in profit while risking $4,750 for a return of 5.26% in one month or 63.15% annualized.
Time decay is $7 per day and gamma is -2. The purple line below is the T+0 line which gives a good estimate of what could happen if the stock drops.
If AAPL drops 2.5% the trade will be down around $250 and if the stock drops 10% the trade will be down around $1,700.
Note that this does not take into account any changes in implied volatility, so the losses would likely be a bit higher than that.
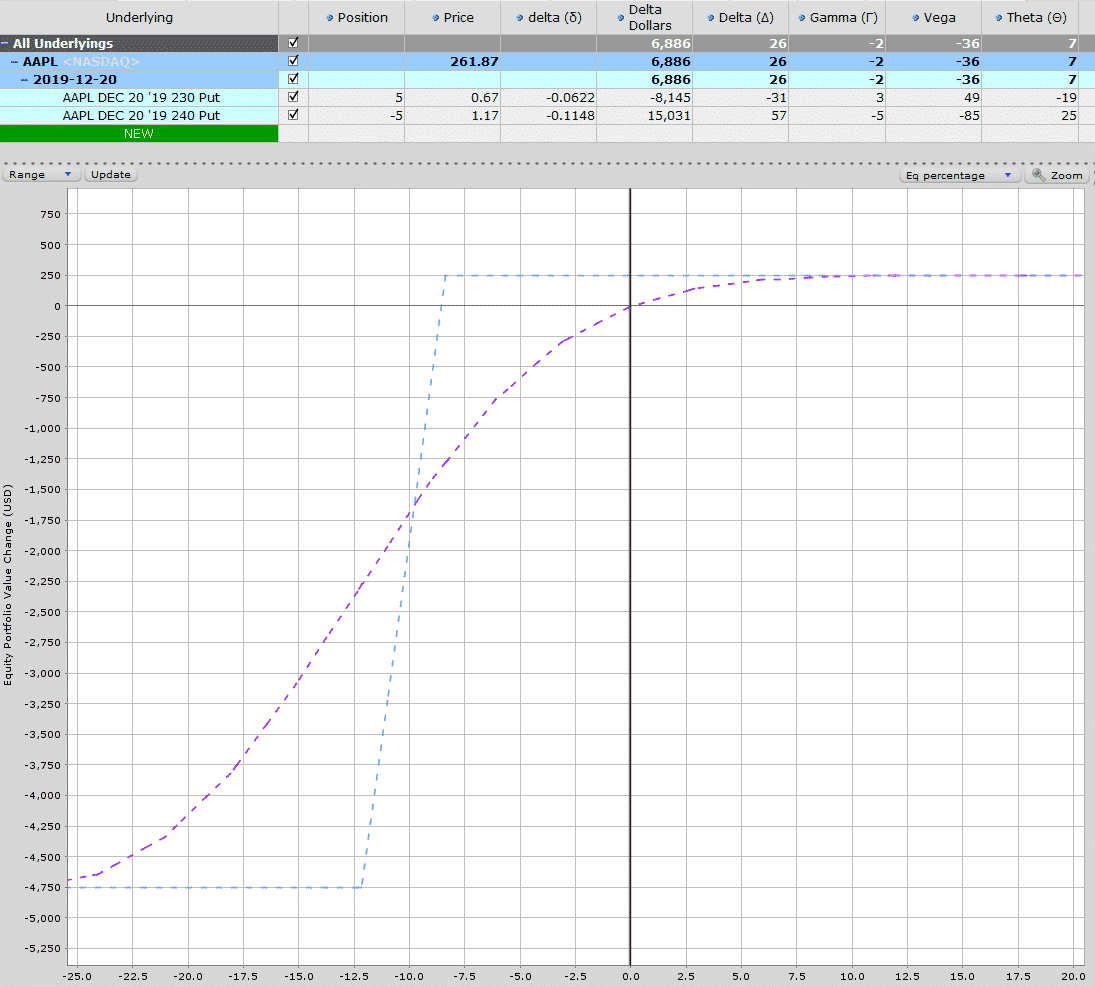
6-MONTH BULL PUT SPREAD
This 6-month trade is also short the 10-delta put and generates slightly more income at $365 with capital at risk of $4,635.
That represents a 7.87% return in 6-months or around 15.75% per annum. That’s still a pretty nice return in my books for a trade that will move a lot slower.
Time decay is $2 per day and gamma is basically zero.
Notice the slop of the T+0 line is much less severe than the 1-month trade.
If AAPL drops 2.5%, this trade would be down around $100 and if it dropped 10% the trade would be down about $550-600, much better than $1,700!
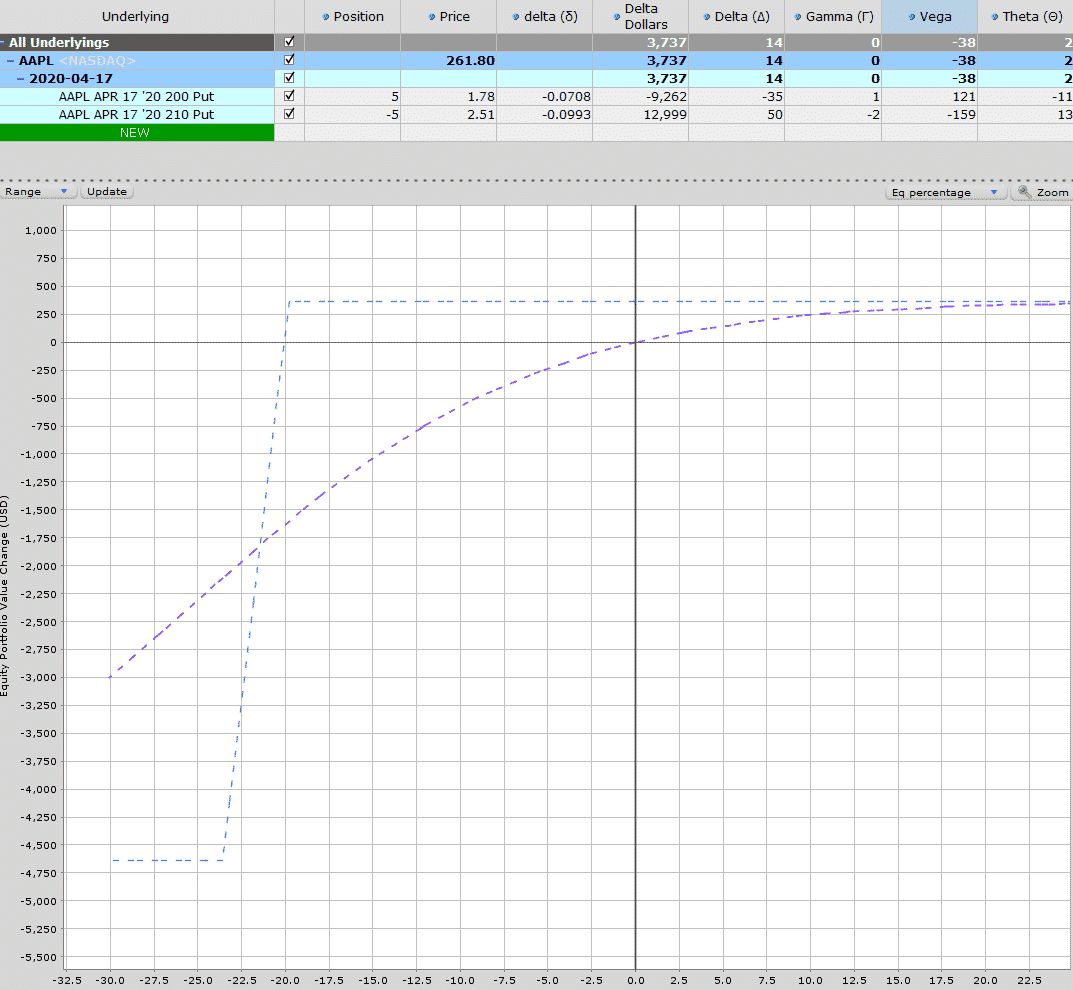
IYR bear call spread example – getting direction wrong but still A winning trade
Back in june 2019, I started to get bearish on REIT’s after they had rallied 28% in 6 months. I even wrote about it here.
On just 20th, I entered a bear call spread on IYR.
At the time, the stock was trading at $90.87 and I sold some december 2019 $95-$100 call spreads.
Date: june 20 th , 2019
Current price: $90.87
Trade set up:
Sell 2 IYR december 20th, 95 calls @ $1.14
buy 2 IYR december 20th, 100 calls @ $0.29
Premium: $170 net credit
Capital at risk: $830
Return potential: 20.48%
Initially, the trade started to work for me as IYR fell to just below $86, but then the ETF rallied back and continued to grind higher over the next few months.
On october 21st, IYR closed at $95.36 and the bear call spread was down $220. I don’t like letting credit spreads go in-the-money, but I will let that happen sometimes with these long-term trades.
In this case I still felt like there would be a pullback at some point before december expiry and that proved to be the case with IYR dropping down to $91 by november 8 th .
I closed the call spread for $0.16 on november 15 th with IYR trading around $92.50. The initial spread was sold for $0.85 and closed for $0.16 for a total profit of $0.69 or 16.63% on capital at risk in about 5 months.
Not bad for a bearish trade where the underlying asset rallied 1.79% between trade initiation and close out.
Conclusion
Trading credit spreads for income is an incredibly popular strategy with income traders. Here are some of the key takeaways from today’s article:
- Credit spread option strategies generate premium because the sold option has a higher value than the bought option.
- Credit spreads can still be profitable if the underlying stock moves against you, as long as it doesn’t move too much.
- Trades can be placed on a directional (bull put or bear call) or neutral basis (iron condor).
- Weekly credit spreads can generate significant income in a short space of time, but they can be risky.
- Long-term credit spreads generate profits more slowly but also lose money at a slower rate if the trade goes against you.
- The best time to enter credit spreads is when implied volatility is high. When this occurs, trades can be placed further away from the stock price giving the trade more margin for error.
I hope you enjoyed this article, please feel free to comment below or share on social media.
Disclaimer: the information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.
Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
Options trading 101 - the ultimate beginners guide to options
Download the 12,000 word guide
It's free
Options trading 101 - the ultimate beginners guide to options
Download the 12,000 word guide

Credit spread option strategies are hugely popular with income traders as they can generate profits in multiple conditions.
In this article I’ll briefly discuss the 3 strategies, show you how they’re set up and then I’ll show you some real examples, so you can see how each of the strategies performs relative to changes in the stock price over time.
Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit spreads
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror stories
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example
- Conclusion
Introduction
Credit spreads, or vertical spreads as they are sometimes called are high probability trades and can profit in more than one way.
They can even profit if the stock moves against you, as long as it doesn’t move too far, as you will see shortly.
Credit spreads can profit in the following ways:
- Favorable movement in the stock price
- Small, unfavourable movement in the stock price
- Time decay
- Decrease in implied volatility
The best time to enter credit spreads is when implied volatility is high. When this occurs, trades can be placed further away from the stock price giving the trade more margin for error.
What is A credit spread?
A credit spread is an option strategy that involves selling an option and then buying a further out-of-the-money option in the same expiry period.
Credit spreads are an income strategy, because premium is collected when initiating the trade. This is because the option that is being sold has a higher premium than the option that is being bought.
Assuming we are bullish on the S&P 500 over the next month, we could sell a put credit spread on SPX.
Typically, this would be below the market. Some people like to use the 10 delta or the 15 delta as the short strike.
Using the 15 delta, the setup would look something like this:
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $3,132
Trade set up:
Sell 1 SPX december 20th, 3025 put @ $8.30
buy 1 SPX december 20th, 3000 put @ $6.50
Premium: $180 net credit
Capital at risk: $2,320
Return potential: 7.76%

Key features of option credit spreads

Put credit spreads
Put credit spreads are a fantastic strategy because stocks tend to rise over time.
This is a strategy that you would implement if you were bullish on a stock or felt that it wouldn’t decline by too much during the trade.
A put credit spread is known as a bull put spread and is constructed by:
- Selling a put option
- Buying another put option at a lower strike price in the same expiry period
Most people trade bull put spreads as out-of-the-money spreads which gives them a good margin for error on the trade.
The further out-of-the-money the trade is placed, the less premium that is received and the higher the capital at risk in the trade.
One regular trade I like to do is a long-term bull put credit spread on dow stocks that have become oversold.
Here’s a trade from early in 2019 on WBA:
Date: april 22nd, 2019
Current price: $54.35
Trade set up:
Sell 10 WBA january 17th 2020, 40 puts @ $0.90
buy 10 WBA january 17th 2020, 35 puts @ $0.40
Premium: $500 net credit
Capital at risk: $4,500
Return potential: 11.11%
Since entering the trade WBA has reached a low of $48.32 in august and in late november was trading at $59.63 with the put credit spread currently sitting at +$440 in P&L.
I’ll look to close the trade out now as there isn’t much premium left and closing the trade can free up the capital for other trades.
Because this was such a long-term trade, it allowed me to place the spread a huge distance away from the WBA price.
At the time, the $40 strike which I sold was 25% below the stock price!

Call credit spreads
Call credit spreads are implemented by traders who think a stock will decline or not rise by much during the trade.
A call credit spread is known as a bear call spread as is constructed by:
- Selling a call option
- Buying another call option at a higher strike price in the same expiry period
The further out-of-the-money the trade is placed, the less premium is received and the higher the capital at risk in the trade.
AAPL is currently one of the most overbought stocks in the dow and looking a little toppy.
While the stock may continue to grind higher, a pullback is definitely overdue and fairly likely at some point in the in the next few weeks.
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $264
Trade set up:
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 300 calls @ $3.07
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 310 calls @ $1.85
Premium: $244 net credit
Capital at risk: $1,756
Return potential: 13.90%
The only downside with this trade is that implied volatility is currently so low in AAPL, that I can’t place the spread as far out-of-the-money as I normally could.
Still, with the short strike at $300, AAPL can rally 13.65% before the short strike is touched.

Iron condor spread
When you combine a put credit spread and a call credit spread, you get a position known as an iron condor.
This is a direction neutral trade and will profit if the stock remains between the two spreads during the course of the trade.
If you want some detailed training on iron condors, you can check out my free course here.
Let’s look at a quick example:
Using our AAPL example, we can add a put credit spread to turn it into an iron condor.
Date: november 26th, 2019
Current price: $264
Trade set up:
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 300 calls @ $3.07
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 310 calls @ $1.85
Sell 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 230 puts @ $3.84
buy 2 AAPL march 20th 2020, 220 puts @ $2.65
Premium: $482 net credit
Capital at risk: $1,518
Return potential: 31.75%
Notice that by generating two lots of premium, we have more than doubled our return potential. You may have also noticed that the capital at risk has decreased.
This is due to the extra premium received while the spreads are the same distance apart.
As above, the only issue with this trade idea is that implied volatility is very low, so it may not be the best time for an iron condor.

Weekly credit spreads for income
Weekly credit spreads can be excellent for generating income, but they are not without risks.
Before we look at the risks, let’s talk about the positives.
The main reason for trading weekly credit spreads is that they provide HUGE amounts of time decay, so profits can be generated very quickly.
Here’s an example of how it works.
This weekly credit spread on AAPL, selling the roughly 10 delta puts, has a theta value of 23. This means that the position will make roughly $23 per day through time decay, all else being equal.

This trade is also selling the 10 delta puts but is a 65-day trade.
The time decay here is only 4$ per day.
As you can see, there is a big difference in the amount of time decay generated from weekly credit spreads compared to monthly or two-month credit spreads.

Notice the difference in gamma as well.
I won’t go into detail now, you can read more about gamma here and here . Just know that the difference between -1 gamma and -6 gamma is significant.
Beginner traders get very excited by the profit potential and fail to realize or fully understand the risk.
There are many websites and “gurus” out there claiming it’s “super easy” to make 5% per week.
Now, anyone with a basic understanding of finance understands that higher returns equal higher risk.
Therefore, if someone is claiming to make 5% per week (which equates to 260% per year), do you think there is much risk involved??
I know my readers are much too smart to fall for those sort of marketing gimmicks, but you would be surprised how many people get sucked in to this way of trading.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve spoken to traders and they all have the same story:
Weekly credit spread horror stories
The stock and timing is different, but the scenario is always the same.
“things were going great, I had 20 winning weeks in a row, and then the market made a big move and BAM, all 20 weeks’ worth of gains were gone, and then some.”
It can happen quickly as well. That gamma risk I talked about earlier, that basically means that even for a small move in the underlying stock, the P&L on the position will move wildly.
That can be great if the stock goes your way, but it can be disastrous if it moves against you.
A high gamma also means that your delta exposure will pick up steam quickly as the position moves against you.
So not only are your losses accelerating, your delta exposure is also getting bigger and bigger.
In a situation like this, there is very little you can do to adjust or save the trade. You can hope the stock reverses, but hope is not a valid strategy.
Monthly credit spreads for income
Monthly credit spreads are also a great option strategy for generating income and they move a lot slower than weekly credit spreads.
This allows you more time to adjust and can give you flexibility by allowing you to stay in the trade longer, even if the stock is moving against you.
One thing I have moved to recently is going even longer term with my credit spreads (see WBA example above).
These trades move very, very slowly, but can still generate excellent returns on an annualized basis with much less stress.
Let’s use AAPL again and compare a 1-month put credit spread and a 6-month put credit spread using the 10-delta strike as the short strike.
1-MONTH BULL PUT SPREAD
This one-month bull put spread has the potential to make $250 in profit while risking $4,750 for a return of 5.26% in one month or 63.15% annualized.
Time decay is $7 per day and gamma is -2. The purple line below is the T+0 line which gives a good estimate of what could happen if the stock drops.
If AAPL drops 2.5% the trade will be down around $250 and if the stock drops 10% the trade will be down around $1,700.
Note that this does not take into account any changes in implied volatility, so the losses would likely be a bit higher than that.

6-MONTH BULL PUT SPREAD
This 6-month trade is also short the 10-delta put and generates slightly more income at $365 with capital at risk of $4,635.
That represents a 7.87% return in 6-months or around 15.75% per annum. That’s still a pretty nice return in my books for a trade that will move a lot slower.
Time decay is $2 per day and gamma is basically zero.
Notice the slop of the T+0 line is much less severe than the 1-month trade.
If AAPL drops 2.5%, this trade would be down around $100 and if it dropped 10% the trade would be down about $550-600, much better than $1,700!

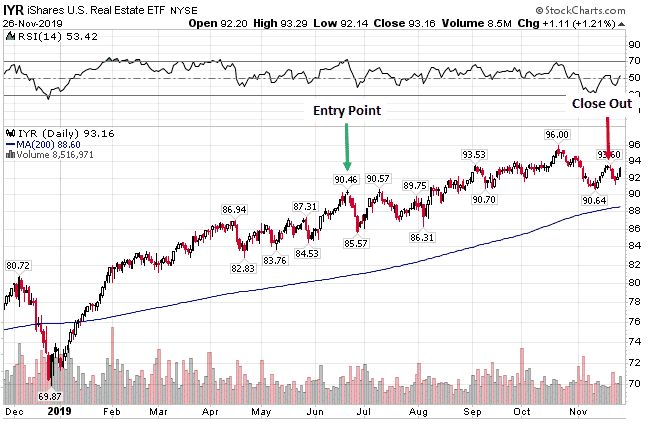
IYR bear call spread example – getting direction wrong but still A winning trade
Back in june 2019, I started to get bearish on REIT’s after they had rallied 28% in 6 months. I even wrote about it here.
On just 20th, I entered a bear call spread on IYR.
At the time, the stock was trading at $90.87 and I sold some december 2019 $95-$100 call spreads.
Date: june 20 th , 2019
Current price: $90.87
Trade set up:
Sell 2 IYR december 20th, 95 calls @ $1.14
buy 2 IYR december 20th, 100 calls @ $0.29
Premium: $170 net credit
Capital at risk: $830
Return potential: 20.48%
Initially, the trade started to work for me as IYR fell to just below $86, but then the ETF rallied back and continued to grind higher over the next few months.
On october 21st, IYR closed at $95.36 and the bear call spread was down $220. I don’t like letting credit spreads go in-the-money, but I will let that happen sometimes with these long-term trades.
In this case I still felt like there would be a pullback at some point before december expiry and that proved to be the case with IYR dropping down to $91 by november 8 th .
I closed the call spread for $0.16 on november 15 th with IYR trading around $92.50. The initial spread was sold for $0.85 and closed for $0.16 for a total profit of $0.69 or 16.63% on capital at risk in about 5 months.
Not bad for a bearish trade where the underlying asset rallied 1.79% between trade initiation and close out.

Conclusion
Trading credit spreads for income is an incredibly popular strategy with income traders. Here are some of the key takeaways from today’s article:
- Credit spread option strategies generate premium because the sold option has a higher value than the bought option.
- Credit spreads can still be profitable if the underlying stock moves against you, as long as it doesn’t move too much.
- Trades can be placed on a directional (bull put or bear call) or neutral basis (iron condor).
- Weekly credit spreads can generate significant income in a short space of time, but they can be risky.
- Long-term credit spreads generate profits more slowly but also lose money at a slower rate if the trade goes against you.
- The best time to enter credit spreads is when implied volatility is high. When this occurs, trades can be placed further away from the stock price giving the trade more margin for error.
I hope you enjoyed this article, please feel free to comment below or share on social media.
Disclaimer: the information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.
So, let's see, what we have: trading credit spreads for a living is a great way to make money while managing risk. We give you a free course on how to trade them. At trading credit
Contents of the article
- My list of forex bonuses
- Trading credit spreads for a living and how to...
- Trading credit spreads for a living & how to get...
- 1. Credit: trading credit spreads for a living
- 2. The pros and cons
- 3. The types of credit spreads
- 4. The goal of trading credit spreads for a living
- Credit trading
- Some of the benefits
- Trade credit
- What is a trade credit?
- Understanding trade credit
- Trade credit accounting
- Trade credit trends
- Related concepts and other considerations
- Crédit agricole trading
- I metodi alternativi al trading offerto...
- Le alternative al trading di crédit...
- Etoro: investire con zero...
- Capital.Com: investire con trading...
- IQ option: investire con le opzioni...
- Caratteristiche dell’offerta crédit...
- Crédit agricole: piattaforme di...
- Crédit agricole: l’offerta di trading...
- Crédit agricole: opinioni e...
- Trade credit
- Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
- Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit...
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror...
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example – getting...
- Conclusion
- Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
- Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit...
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror...
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example – getting...
- Conclusion
Contents of the article
- My list of forex bonuses
- Trading credit spreads for a living and how to...
- Trading credit spreads for a living & how to get...
- 1. Credit: trading credit spreads for a living
- 2. The pros and cons
- 3. The types of credit spreads
- 4. The goal of trading credit spreads for a living
- Credit trading
- Some of the benefits
- Trade credit
- What is a trade credit?
- Understanding trade credit
- Trade credit accounting
- Trade credit trends
- Related concepts and other considerations
- Crédit agricole trading
- I metodi alternativi al trading offerto...
- Le alternative al trading di crédit...
- Etoro: investire con zero...
- Capital.Com: investire con trading...
- IQ option: investire con le opzioni...
- Caratteristiche dell’offerta crédit...
- Crédit agricole: piattaforme di...
- Crédit agricole: l’offerta di trading...
- Crédit agricole: opinioni e...
- Trade credit
- Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
- Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit...
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror...
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example – getting...
- Conclusion
- Top 3 ways to trade credit spreads for income
- Contents
- Introduction
- What is A credit spread?
- Key features of option credit...
- Put credit spreads
- Call credit spreads
- Iron condor spread
- Weekly credit spreads for income
- Weekly credit spread horror...
- Monthly credit spreads for income
- IYR bear call spread example – getting...
- Conclusion
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.